Blog
How to Raise Your Credit Score in 30 Days – 20 Smart Ideas
May 25, 2019
Have you ever wondered how to raise your credit score in 30 days? Obviously, it’s a worthy goal for real estate investors to raise their scores before seeking a loan. Naturally, by performing credit repair, you stand a better chance of getting the funding you want at a good rate. Read on if you would like to know how to improve your credit score. You might be surprised at how quickly you can boost your score. In this article, we reveal 4 ways to boost your credit score instantly, 7 ways to improve your credit score in 30 days, and 5 ways to better your credit score in the long term. Then we discuss 4 ways to prevent credit score losses and answer frequently asked questions. In addition, there’s a substantial section on understanding how credit scoring works,
Video: Amazing Tips on How to Raise Your Credit Score in 30 Days
How to Improve Your Credit Score Instantly
If you want to know how to improve your credit score instantly, you should become familiar with these simple techniques:
1. Get a Credit Card or a Loan
If you don’t already have one, apply for debt right away. If you receive approval, your credit score should benefit immediately. The reason is that your available credit will rise, and reduce your credit utilization ratio (CUR). CUR equals (credit used / credit available). Importantly, the credit bureaus like to see low CURs, preferably below 30%.
2. Remove tax liens
Tax liens can really weigh down your credit score. It’s one of several derogatory items that cripple your credit. Naturally, if you pay off your tax debt and lose the lien, your score should immediately benefit.
3. Join Experian BoostAmerica
This is a program that Experian offers to help consumers boost their scores quickly. Specifically, the program lets you report your bill payments for cable, cell phone usage, utilities and other items. Previously, you couldn’t get credit for paying these bills on time. Now, thanks to Experian, you can. Thankfully, that could have an immediate positive effect on your score.
4. Join TransUnion CreditCompass
You can sign up for TransUnion CreditCompass, a program that recommends steps to boost your credit score. When you join, you’ll receive credit monitoring and your current score. Then, you set your target score and receive credit repair suggestions from TransUnion to achieve your goal.
Apply For Financing
How to Raise Your Credit Score in 30 Days
How to raise your credit score in 30 days? There are several things you can do that will improve your score quickly, including:
5. Fix Your Credit Report
All three nationwide credit bureaus must respond to complaints about mistakes and omissions on your credit report. The bureaus are Equifax, TransUnion and Experian. They understand that errors can depress your credit score needlessly. By correcting the record, you will remove an anchor pulling down your score.
6. Reduce Your Unpaid Balance
As we mentioned earlier, your credit score benefits when your credit utilization rate falls. By paying down your debt, you reduce your utilization of credit, and thereby drive down your CUR. An initial CUR target of 30% is good, but 20% is even better. Clearly, you might have to live lean for a while, but it’s worth it to force down your CUR.
7. Pay Semi-Monthly
Creditors report your activity to the credit bureaus once a month. Now, imagine you run up a large balance early in the month. Furthermore, suppose creditors report that high balance before you have a chance to pay it off later that month. Inevitably, it will look like you are chronically overusing your credit. If you pay every half-month, your running balance will be lower. Moreover, the bureaus won’t ding you for a phantom high balance.
8. Request a Higher Credit Limit to Help Raise Your Credit Score
This is yet another tactic to lower your credit utilization rate. By increasing your available credit and not spending it all right away, your CUR will go down. Logically, if you increase your credit limit, spending the increase defeats the whole purpose of the exercise. Therefore, leave your increased credit unspent to reap the rewards of a lower CUR.
9. Open an Additional Account
This too will reduce your CUR as long as you don’t use too much of your additional credit. Beware, opening multiple accounts in a short period can hurt (lower) your credit score. It gives the impression that you are in a financial pickle, and that’s not good for your credit score. Therefore, just add one or two new accounts to help reduce your CUR.
10. Clean up Past Due Bills
To raise your credit score, cleaning up tax liens isn’t enough. Truthfully, any bill that is past due can sink your score. Extricate yourself from this losing situation by paying off all past-due bills. One strategy is to get a new credit card that offers an introductory 0% APR on balance transfers for up to 18 months. Next, transfer all your credit card balances to the new card. Now, you’ll only have one credit card bill to pay each month, and you’ll be rid of past-due bills. Alternatively, you can achieve the same effect with a consolidation loan that encompasses all types of debt.
11. Moderate Your Spending
The credit bureaus will notice when your monthly spending recedes. That will lower your CUR and project an impression that you mastered your finances. Cleverly, try using cash for some of your spending so that your credit balances don’t rise. This will put increasing distance between your balance and your credit limit, a positive factor.
Executing the preceding steps are how to raise your credit score in 30 days, give or take.
How to Improve Your Credit Score Long-Term
Now that you’ve addressed how to raise your credit score in 30 days, it’s time to think long-term. Consider the following credit repair steps as examples of how to improve your credit score forever.
12. Become an Authorized User
You might be just starting out in your use of credit. Or maybe, you’ve hurt your credit so badly that no credit card company will approve you. You can establish or reestablish your credit score by becoming an authorized user of someone else’s credit card. Legally, both you and the card owner will get credit for timely payments. Clearly, that should help both of your credits scores. Even though you aren’t legally liable for the debts on the card, never abuse the owner’s trust in you. That is, act responsibly, earn a better score, and more importantly, keep your trusted friend or loved one!
13. Obtain a Secured Card
You can qualify for a secured card by depositing money into an account to act as collateral. Your credit line is the amount of the deposit, within the issuer’s limits. Usually, by using the card responsibly for six months or so, you likely will qualify for an unsecured card.
14. Blend Your Credit
The credit bureaus like to see a mix of different types of debt. For example, your score would benefit by having revolving, personal and installment debt on your credit report.
15. Get a Cosigned Loan
Apply for a personal loan with the help of a cosigner. This will help you reestablish your financial reputation. Of course, you need to repay this loan on time, or even ahead of time. Afterward, you can take out another personal loan, this time without a cosigner.
16. Buy real property
Now that you’ve shown your creditworthiness, it’s time to buy real estate. For example, you might consider a fix-and-flip deal. These are easy to finance because the property serves as collateral and the down payment is relatively large. Then, you can graduate to a long-term deal to earn rental income. Use the income to pay down the mortgage, which will be a big boost for your score. Eventually, you’ll be ready for deals of $20 million or more.
When that happens, you should contact us at Assets America® as our minimum loans start at $20 million! We can then help you arrange all types of commercial real estate loans, whether construction, rehab, or acquisition. Our brokerage partners will get you the money you need for sensible real estate deals.
Preventing Future Losses
Here are some steps you should take to prevent a future dip in your credit score:
17. Pay Your Bills on Time
It’s critical that you pay at least the minimum payments each month on your debts. Naturally, this covers all your bills, as any late payment will be promptly reported on your credit report thus damaging your score.
18. Don’t Close Old Accounts
Just because you no longer need or use a revolving account, that’s no reason to close it. Rather, by leaving it open, you don’t truncate your credit history and you maintain your CUR. The credit bureaus like the continuity of long-held accounts, so leave them be even if they seem obsolete.
19. Use Shell Corporations and Nonrecourse Loans
The last thing you want is for bad business decisions to hurt your personal credit score. Therefore, be sure to keep your business debt remote from your personal identity. Use nonrecourse financing and shell corporations to keep your identity obscure. In this way, you can take the risks necessary to win at business without potentially jeopardizing your personal credit.
20. Consider Relocation
Many successful real estate developers and businesspersons relocate to one of the many wonderful tax havens available. You might choose locations in the Caribbean, Europe or Asia as a place to work and live. Many expatriates give up their American citizenship to become subjects of Lichtenstein, the Cayman Islands or another tax-friendly jurisdiction. If you want to prevent future threats to your credit score, you may wish to consider doing it as a citizen of the world. However, it then makes obtaining U.S. credit much more difficult!
Questions to Answer to Raise Your Credit Score in 30 Days
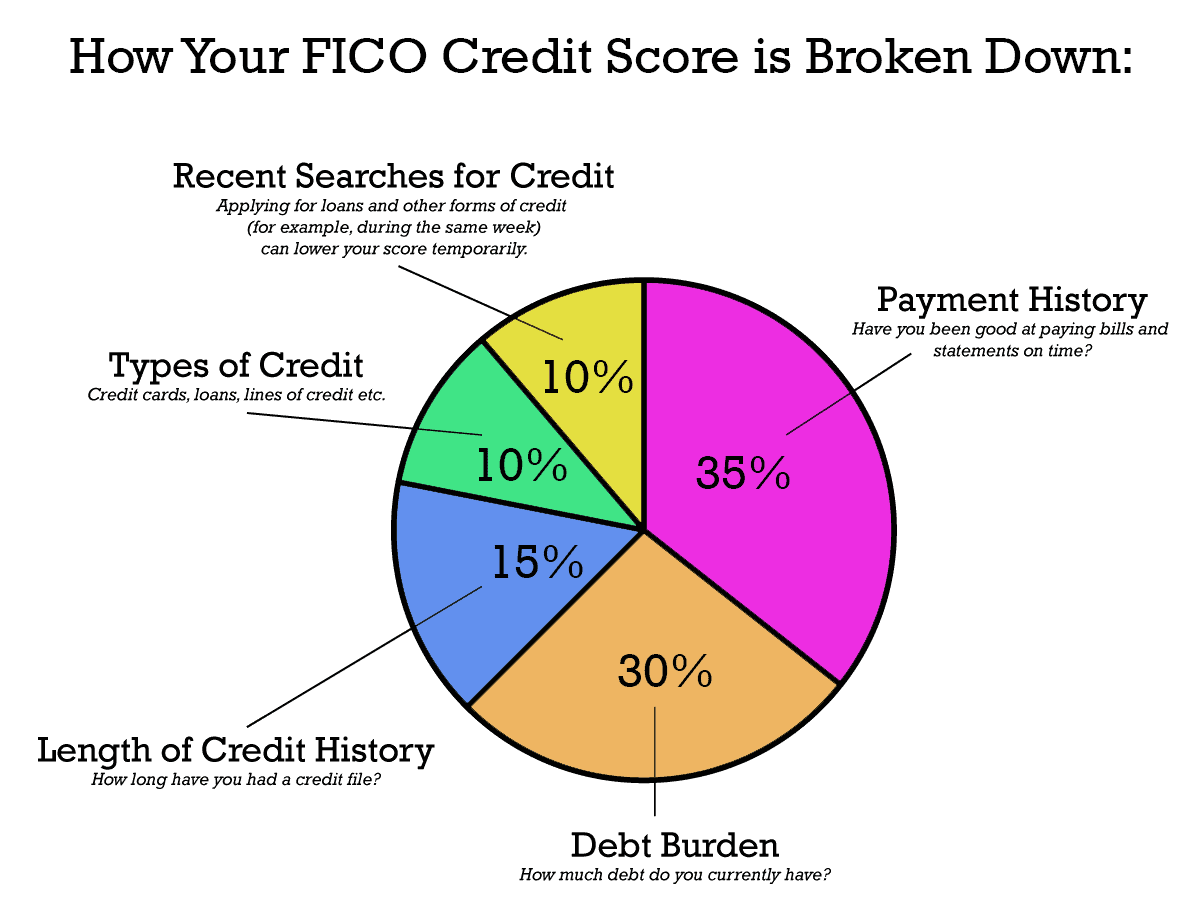
Credit scoring models are complex and often vary among creditors and for different types of credit. If one factor changes, your score may change — but improvement generally depends on how that factor relates to other factors considered by the model. Nevertheless, scoring models generally evaluate the following types of information in your credit report:
What is your outstanding debt?
Many scoring models evaluate the amount of debt you have compared to your credit limits. If the amount you owe is close to your credit limit, that is likely to have a negative effect on your score.
How long is your credit history?
Generally, models consider the length of your credit track record. An insufficient credit history may have an effect on your score, but that can be offset by other factors, such as timely payments and low balances.
Have you applied for new credit recently?
Many scoring models consider whether you have applied for credit recently by looking at “inquiries” on your credit report when you apply for credit. If you have recently applied for numerous new accounts, that may negatively affect your score. However, not all inquiries are counted. Inquiries by creditors who are monitoring your account or looking at credit reports to make “prescreened” credit offers are not counted.
How many and what types of credit accounts do you have?
Although it is generally good to have established credit accounts, too many credit card accounts may have a negative effect on your score. In addition, many models consider the type of credit accounts you have. For example, under some scoring models, loans from finance companies may negatively affect your credit score.
Scoring models may be based on more than just information in your credit report. For example, the model may consider information from your credit application as well: your job or occupation, length of employment, or whether you own a primary residence.
To improve your credit score under most models, concentrate on paying your bills on time, paying down outstanding balances, and not taking on new debt. It’s likely to take some time to improve your score significantly.
What Happens If You’re Denied Credit or the Terms You Want?
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act requires creditors to give you a notice that tells you the specific reasons your application was rejected. You have the right to learn the reasons of your rejection, if you ask within 60 days. Indefinite and vague reasons for denial are illegal, so ask the creditor to be specific. Acceptable reasons include: “Your income was low” or “You haven’t been employed long enough.” Unacceptable reasons include: “You didn’t meet our minimum standards” or “You didn’t receive enough points on our credit scoring system.”
If a creditor says you were denied credit because you are too near your credit limits on your charge cards or you have too many credit card accounts, you may want to reapply after paying down your balances or closing some accounts. Though sometimes closing accounts may have a derogatory effect on your credit score. Credit scoring systems consider updated information and change over time.
Understanding the Credit Scoring System
If you still need more information on how to improve your credit score in 30 days, it may be helpful to get a behind-the-scenes look at the system. Read on to discover important topics like the definition of credit scoring, why it’s used, how credit scoring models are developed, the reliability of credit scores, the fair credit reporting act, your legal rights, the information credit bureaus collect and sell, and more FAQs. By giving yourself perspective on the system as a whole, you may enable yourself to boost your credit score in a month or less.
What Is Credit Scoring?
Credit scoring is a system creditors use to help determine whether to offer you credit. Information about you and your credit experiences, such as your bill-paying history show on your report. Further information includes the number and type of accounts you have, late payments, collection actions, outstanding debt, and the age of your accounts. This is all collected from your credit application and your credit report. Using a statistical program, creditors compare this information to the credit performance of consumers with similar profiles. A credit scoring system awards points for each factor that helps predict who is the most likely to repay a debt. It also awards points for people who repay that debt in a timely and methodical fashion.
A total number of points — a credit score — helps predict how creditworthy you are. That is, how likely it is that you will repay a loan and make the payments when due. Your credit report is an important part of many credit scoring systems. Therefore, it is very important to make sure it’s accurate before you apply for a commercial loan. To get copies of your report, contact the three major credit reporting agencies:
Equifax: (800) 685-1111
Experian (formerly TRW): (888) EXPERIAN (397-3742)
Trans Union: (800) 916-8800
These agencies may charge you $9.00, or more for your credit report, although they can be free.
Why Is Credit Scoring Used?
Credit scoring is based on real data and statistics, so it usually is more reliable than subjective or judgmental methods. It treats all applicants objectively. This purportedly “objective” scoring method may or may not beneficial to all commercial loan applicants. Typically, judgmental methods rely on various criterion. These are not systematically tested and can vary when applied by different individuals.
How Is a Credit Scoring Model Developed?
To develop a model, a creditor selects a random sample of its customers, or a sample of similar customers if their sample is not large enough, and analyzes it statistically to identify characteristics that relate to creditworthiness. The CRAs assign a weight to each of these factors. It is based on how strong a predictor it is of who would be a good credit risk. Each creditor may use its own credit scoring model, different scoring models for different types of credit, or a generic model developed by a credit scoring company. Under the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, a credit scoring system may not use certain characteristics like — race, sex, marital status, national origin, or religion — as factors. However, creditors are allowed to use age in properly designed scoring systems. But any scoring system that includes age must give equal treatment to elderly applicants.
How Reliable Is the Credit Scoring System?
Credit scoring systems enable creditors to evaluate millions of applicants consistently and impartially on many different characteristics. But to be statistically valid, credit scoring systems must be based on a large enough sample. Remember that these systems generally vary from creditor to creditor. Although you may think such a system is arbitrary or impersonal, it can help make decisions faster, more accurately. It is more impartial than individuals, that is, when it is properly designed. And many creditors design their systems so that in marginal cases, applicants whose scores are not high enough to pass easily or are low enough to fail absolutely are referred to a credit manager who decides whether the company or lender will extend credit. This may allow for discussion and negotiation between the credit manager and the commercial loan applicant.
What is the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)?
Sometimes you can be denied credit because of information from a credit report. If so, the Fair Credit Reporting Act requires the creditor to give you the name, address and phone number of the credit reporting agency that supplied the information. You should contact that agency to find out what your report said. Request your credit report within 60 days of being turned down for credit. That way, it’s free. The credit reporting agency can tell you what’s in your report, but only the creditor can tell you why your application was denied.
If you’ve been denied credit, or didn’t get the rate or credit terms you want, ask the creditor if a credit scoring system was used. Then, ask what characteristics or factors were used in that system, and the best ways to improve your application. If you get credit, ask the creditor whether you are getting the best rate and terms available for your commercial mortgage application and, if not, why. Inaccurate credit information can cause lenders to offer substandard interest rates to you. Therefore, be sure to dispute any inaccurate information in your credit report.
Do I Have a Right to Know What’s in My Report?
Yes, if you ask for it. The Credit Rating Agency must tell you everything in your report. This would include medical information, and in most cases, the sources of the information. The CRA also must give you a list of everyone who has requested your report within the past 2 years. This would also include information for employment related requests.
What Type of Information Do Credit Bureaus Collect and Sell?
Credit bureaus collect and sell four basic types of information:
Identification and employment information
Credit Rating Agencies routinely note your name, birth date, social security number, employer, and spouse’s name. The CRA also may provide information about your employment history, home ownership, income, and previous address. That is, if a creditor requests this type of information.
Payment history
Different creditors list your accounts. They show how much credit has been extended and whether you’ve paid on time. Related events, such as referral of an overdue account to a collection agency, may also be noted.
Inquiries
CRAs must maintain a record of all creditors who have asked for your credit history within the past 2 years. Also, records of those persons or businesses requesting your credit history for employment purposes show for the past two years.
Public record information
There are events that are a matter of public record. Bankruptcies, foreclosures, and tax liens may appear in your report as well.
In conclusion, we hope this article has provided you with the ultimate resource on how to raise your credit score in 30 days. We have provided an exhaustive list of ideas on how to improve your credit score rapidly, in addition to general information on the credit scoring system. Hopefully these frequently asked questions enable you to raise your credit score in 30 days without a hitch!
FAQs: How to Raise Your Credit Score in 30 Days
What is an overall good credit score?
Generally, good scores are in the 700 to 799 range on the FICO scale. Better yet, we call scores between 800 and 850 excellent. If you’d like to develop or invest in real estate, your minimum goal is to establish a good credit score.
What is a good credit score for commercial real estate?
Even though a score above 720 is preferred for commercial real estate, it’s not mandatory. You can access hard money loans with scores as low as 550, and sometimes even lower. A lot depends on the nature of the deal and the value of the collateral relative to the loan size.
How do I improve my credit score after Chapter 7?
You should probably consider getting secured and cosigned debt. Making your payments on time will help you recover your score over time, though it might take several years. The effects of bankruptcy are immediate but begin to fade after two or three years.
Does paying off collections improve my credit score?
Surprisingly, the answer is no. Collections do grave damage to your credit score, second only to bankruptcy. In fact, it’s so bad, that paying off a collection has little chance of improving your score. Nonetheless, you should pay off the debt and note it on your credit report. Undoubtedly, this will impress future lenders.